In addition to being an important technology sector in its own right, information and communication technology (ICT) is important for linking agents in the innovation system. The Addis Ababa Action Agenda promotes the use of ICT, greater access to technology for all and social innovation.
The Addis Agenda specifically:
- Commits to promote the development and use of information and communications technology, particularly in LDCS, LLDCs and SIDs, including rapid universal and affordable access to the Internet
- Commits to further facilitate accessible technology for persons with disabilities and to promote access to technology and science for women, youth and children
- Commits to promote social innovation to support social well-being and sustainable livelihoods
Latest developments
Deploying new technologies could be transformative for the sustainable development agenda, as they offer solutions that are better, cheaper, more scalable and faster to replicate. They can raise productivity, increase environmental sustainability and improve the delivery of basic services. Artificial intelligence (AI) is the technology that has received the most attention from researchers, as measured by the number of publications, which totalled over 400,000 between 1996 and 2018. Robotics followed, with over 250,000 publications in the same period. AI also accounts for the largest number of patents filed during those years, followed by the Internet of things (IoT).
Read more on new and emerging technologies and the SDGs here.
New and emerging technologies have already begun to transform the financial sector, and fintech has been an important driver of financial inclusion. Developments in financial technology have been shaped by country-specific conditions, including differences in the availability and quality of necessary infrastructure and complementary technology, as well as financial sector characteristics and regulatory standards. As a result, fintech growth has been uneven among countries and regions.
Read more on fintech trends and financial inclusion here.
See also financing sustainable development in an era of transformative digital technologies here.
Globally, the number of broadband subscriptions is on the rise, although with a different pattern between developed and developing countries. While in developed countries, there are now 36 fixed broadband connections for every 100 persons, developing countries only reach 11 connections per 100 inhabitants, and LDCs only 2. On the other hand, mobile broadband connections are rising faster in developing countries, reaching 75 connections per 100 inhabitants. As a result, the number of people using the Internet continues to grow, reaching 54 per cent of the global population in 2019. The gap between developed and developing countries has narrowed considerably, especially for Latin America and the Caribbean, Western Asia, and East and Southeast Asia.
Percentage of individuals using the Internet, 2006 and 2017
(Percentage)
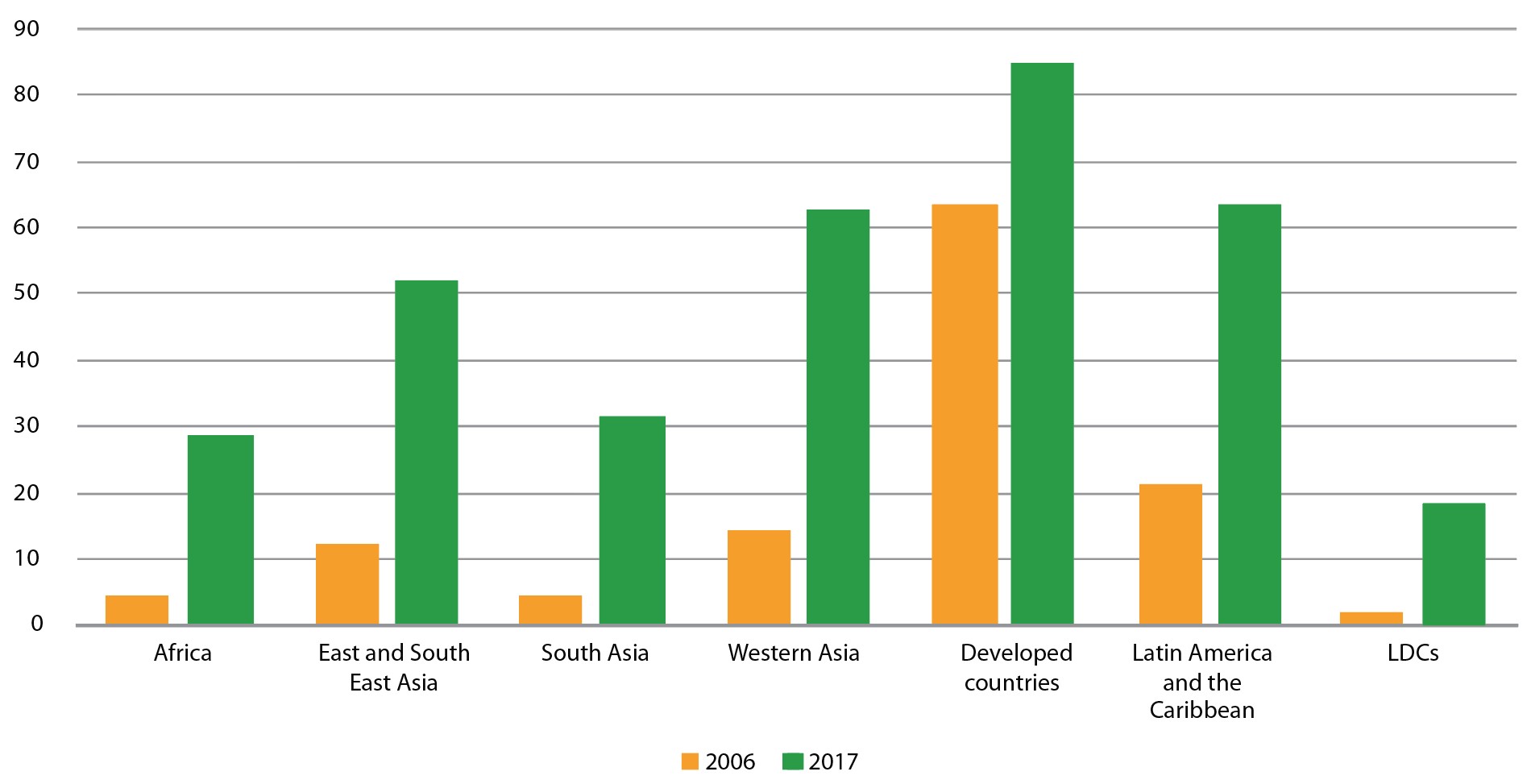
Source: UNCTAD, based on ITU.
Read more on the latest trends by the Task Force here.
Relevant SDG indicator
- 4.4.1 Proportion of youth and adults with information and communications technology (ICT) skills, by type of skill
- 4.a.1 Proportion of schools with access to: (a) electricity; (b) the Internet for pedagogical purposes; (c) computers for pedagogical purposes; (d) adapted infrastructure and materials for students with disabilities; (e) basic drinking water; (f) single-sex basic sanitation facilities; and (g) basic handwashing facilities (as per the WASH indicator definitions)
- 5.b.1 Proportion of individuals who own a mobile telephone, by sex
- 9.c.1 Proportion of population covered by a mobile network, by technology
- 17.6.2 Fixed Internet broadband subscriptions per 100 inhabitants, by speed
- 17.8.1 Proportion of individuals using the Internet